Thomas R. Marshall is not a household name anymore, even in his native Indiana. But a hundred years ago, from 1913 to 1921, this former Hoosier governor served as Vice President of the United States. If Woodrow Wilson had ever died in office, Marshall would have become Indiana’s second native son to serve as Commander-in-Chief.
As fate had it, though, the Vice President himself had to contend with threats from “cranks” and would-be assassins. Most were probably hoaxes. But the man who actually dynamited Marshall’s office in 1915 turned out to be a strange “crank” indeed.
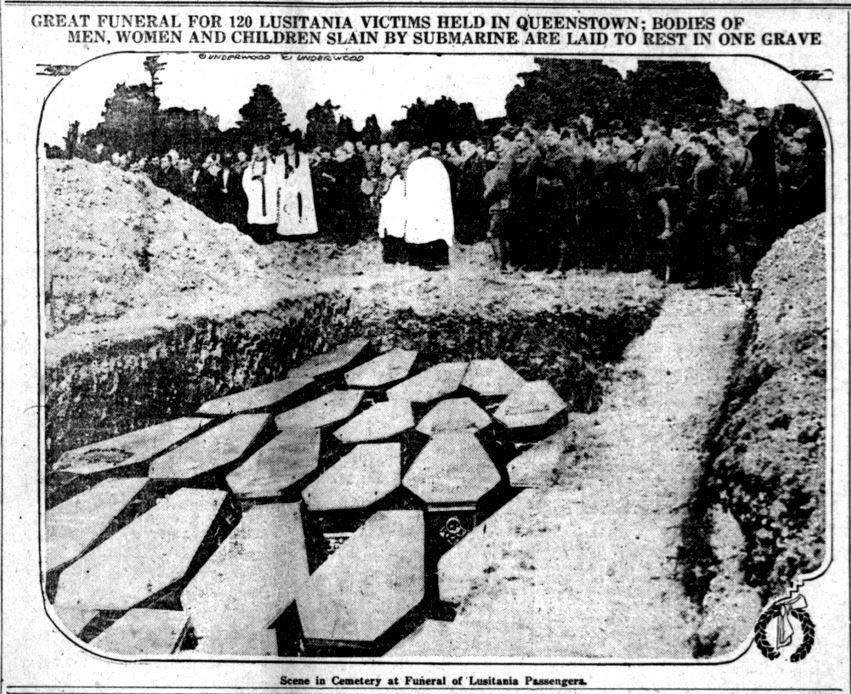
Anti-government and anti-capitalist terrorism in the U.S. has been around for generations — and its earliest practitioners weren’t Muslim. During the early 1900s, numerous bomb plots originating with the American labor movement targeted both high government officials and Wall Street. Union men carried out a deadly plot on the Los Angeles Times building in 1910. A Polish-American anarchist from the Midwest assassinated William McKinley in 1901. Anarchists also targeted industrialists, the occasional high churchman, and came close to blowing up St. Patrick’s Cathedral in New York in 1915. (This week, in fact, marks the 100th anniversary of the anarchist “soup plot” that would have been Chicago’s worst mass murder.)
In July 1915, just a few days after an explosion rocked the U.S. Senate outside his private office there, the V.P. told the press that he had been getting death-threats in the mail for at least six weeks. Marshall considered himself “more or less a fatalist” and ignored these threats from “cranks.” He threw the letters in the trash and never even informed the Secret Service.

(Indianapolis Star, July 5, 1915.)
Because those letters went straight to the waste bin, it’s hard to say if there was any connection to the man who dynamited the Senate just outside his private office door a few minutes before midnight on July 2, 1915.
If John Schrank and John Hinckley’s motivation behind their attempts to shoot Teddy Roosevelt and Ronald Reagan seemed far-fetched — Schrank was told to do it by the ghost of William McKinley in a dream, and Hinckley wanted to impress actress Jodi Foster — the story behind Erich Muenter’s attack on the U.S. Capitol is even weirder.
At a time when nativists wanted to shut off immigration to the poor, Muenter — an immigrant — had taught at Harvard and Cornell. He was also a wife-murderer, an Ivy League scholar, and lived an incredible double-life. Maybe the expert on German literature knew a bizarre tale by E.T.A. Hoffmann, The Life and Opinions of Tomcat Murr, told when a printer accidentally spliced together an artist’s autobiography and the views of an opinionated tomcat.
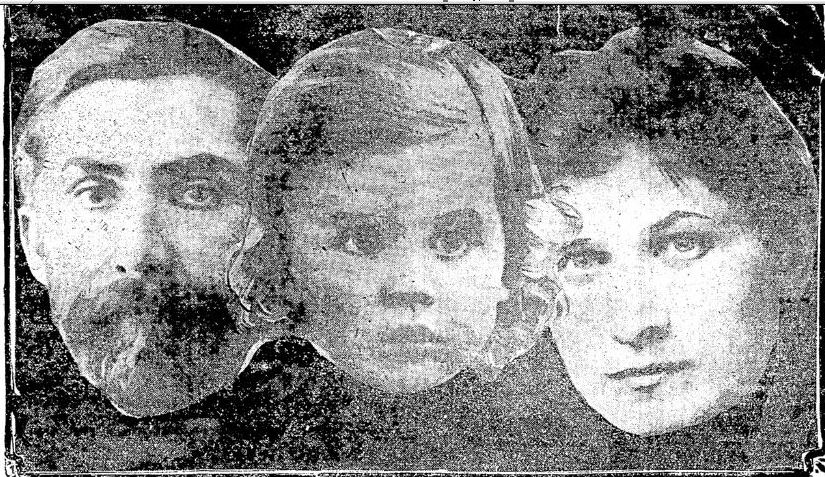

(The bomber Muenter, left, first came to notoriety in 1906, when he poisoned his wife Leona just days after she gave birth to their daughter.)
Erich Muenter was born in Germany and immigrated to Chicago with his parents at age eighteen. He studied languages at the University of Chicago, graduating in 1899, then taught at the University of Kansas for a year before moving to Harvard in 1904, where he was a star doctoral student. In Chicago in 1901, he had married Leone Krembs, daughter of a rich Milwaukee druggist. Friends in Kansas considered Muenter brilliant and thought that he knew virtually “every living language.” The Muenters were hugely popular with students and faculty both at Kansas and Harvard.
The couple, it is thought, were “mystics” and Christian Scientists, rejecting medication in favor of faith healing. When Leone died in Cambridge, Massachusetts, in April 1906, a few days after giving birth to a daughter, Muenter — who had been slowly poisoning her with arsenic — thought that Christian Science gave him the perfect cover-up, but hastily tried to ship the body to Leona’s parents in Chicago for burial. A Massachusetts doctor, however, performed a secret autopsy and uncovered traces of poison in her stomach.
Now dubbed the “Harvard wife murder,” Muenter fled from the law. In spring 1906, he became a national news sensation, with some papers touting spectacular, tabloid-like theories about why he had killed his wife. One theory had it that Muenter, like Goethe’s Faust, was a “slave to science” and had taken the hunt for knowledge too far.


(The Pittsburgh Press, April 29, 1906.)
Guilty or not, the fugitive eventually slipped over the border to Mexico, where he hid out for a few years, working as a bookkeeper at a mining operation outside Mexico City.
Some time before 1912, under the alias “Frank Holt,” he came back to the U.S. and re-invented himself — as another version of Erich Muenter. Holt, incredibly, even enrolled at Texas Tech as an undergrad in the German department. The former Harvard instructor naturally shone as a star student in College Station. And Muenter/Holt must have had a thing for women named Leona, since he married a fellow language student, Leona Sensabaugh, daughter of a prominent Methodist minister in Dallas. The Holts had three children together. Leona Holt went on to teach Latin American literature at Southern Methodist University and eventually became its dean of women.
After teaching at SMU himself, Frank Holt returned to the Ivy League, landing positions at Vanderbilt and Cornell. So it was that less than a decade after he killed his first wife, he returned to academia… by another route and as another man.

(The Fort Wayne News, July 8, 1915.)
Muenter/Holt had also become a German nationalist. Though President Wilson was trying hard to keep America out of the bloodbath of World War I, many Americans thought the U.S. should enter on the side of Britain. Others favored Germany. Socialists almost universally opposed any American involvement at all, arguing that the war only played into the interests of Wall Street. Anarchists agreed.
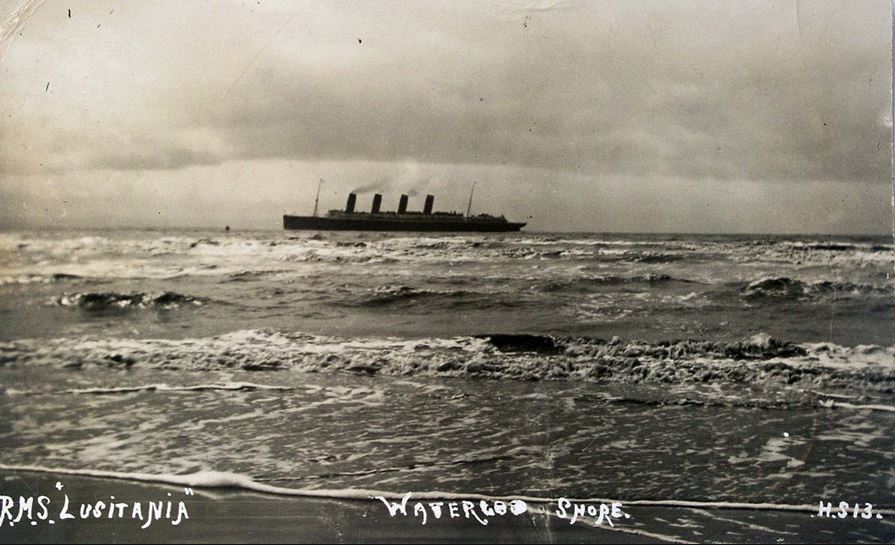
Some pro-British Americans were already turning a profit from the war by shipping munitions to the Allies, often secretly. A load of illegal explosives allegedly sent aboard the passenger liner Lusitania led a German U-Boat to torpedo it just two months before Erich Muenter dynamited the Senate. Germany and its U.S. sympathizers considered this version of “neutrality” a sham. Some went to extremes to protest it.
In 1915, “Frank Holt,” Cornell University professor, read a book by a former Harvard colleague of his — from back when Holt was Erich Muenter. The book was The War and America by Hugo Münsterberg, a well-known pioneer in forensic psychology and a German sympathizer. (In 1918, Münsterberg’s book showed up on a list of pro-German works banned from Indiana libraries.) Convinced by Münsterberg’s argument and angered by American financiers’ profiting off the war, Frank Holt offered his services to the American branch of the German intelligence unit Abteilung IIIB. Founded in 1889, this was a long-standing military spy unit, but during World War I it worked to sabotage arms-carrying vessels departing from U.S. ports. The unit also allegedly supported Erich Muenter’s attack on the Capitol Building — then on J.P. Morgan, Jr., Wall Street mogul.

On the night of July 2, 1915, Muenter broke into the Capitol with three sticks of concealed dynamite. The Senate was actually out of session and few people were in the building other than a nightwatchman. Finding the door to the Senate chamber locked, Muenter set the package under a telephone switchboard next to Vice President Marshall’s office. Reports differ, but the attacker then either set the timer for just before midnight “to minimize casualties” or the timer went off eight hours early. He then boarded a train from Union Station bound for New York City.
The blast that ensued at 11:23 PM rocked the Capitol. The watchman and other witnesses thought the great dome was collapsing. In reality, damage spread little farther than the Senate Reception Room and Thomas Marshall’s office. No one was injured.
Using a pseudonym, Muenter mailed a letter to The Washington Evening Star, expressing anger at American financiers. The dynamiter argued that he didn’t want to kill anybody, even posing as a friend to America who wanted to save lives and “make enough noise to be heard above the voices that clamor for war. This explosion is an exclamation point in my appeal for peace.” Some papers later called him a “Christian” and a “peace crank.” The anti-war American Socialist press even appears to have sympathized with Holt.

(Socialists — like James Larkin Pearson, editor of North Carolina’s satirical The Fool-Killer, were almost always against the war. Indiana Socialist and presidential candidate Eugene V. Debs went to prison for speaking out against it.)
Indiana’s Thomas Marshall confessed that “he naturally was startled when he heard of the explosion at the Capitol,” but didn’t think there was any “special significance” in the fact that the dynamite had been placed “within a few feet of his desk.” Muenter, in fact, was probably bluffing when he told the police that he’d sought to blow up the Vice President. Marshall was headed to St. Louis and Hot Springs, Arkansas, for Fourth of July festivities.

(The Topeka Daily Capital, July 5, 1915.)

(Marshall, former Hoosier governor, at his office in the Senate. The blast occurred a few feet from where this photo was taken.)
J.P. Morgan, Jr., son of the great financier John Pierpont Morgan, was less fortunate than Marshall. If Americans in 2016 are outraged by the actions of “banksters” and the “1%,” so too was Erich Muenter/Frank Holt a century ago — alongside many Americans less prone to engage in political assassination.
The morning after the Senate bombing, Muenter broke into Morgan’s estate on Long Island. An epitome of Wall Street, “Jack” Morgan was already reeling in millions of dollars from war loans to the Allies. He also arranged for ammunition from American manufacturers to be shipped on vessels to Britain. Regardless of what side was right or wrong in that war (probably neither was), Morgan’s profiteering jeopardized “neutral” shipping and American lives on the high seas.
Angry at the millionaire, the strange language instructor — who had committed murder once before — took a gun and broke into Morgan’s mansion, where the Wall Street tycoon was having breakfast with the British ambassador, Sir Cecil Spring Rice. Muenter shot Morgan twice before servants subdued him with a lump of coal. Press headlines announced that the “war-crazed crank” had also planned to take Morgan’s wife and children hostage until he and other tycoons agreed to stop financing the Allies.
The banker survived. Muenter was hauled off for interrogation by the NYPD’s Bomb Squad, which normally tried to protect New Yorkers from attacks by anarchists.
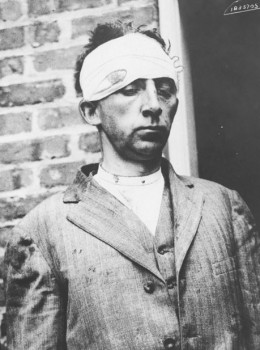
(Muenter in police custody.)

(The Fort Wayne Journal-Gazette, July 4, 1915.)
Early reports on the events in Washington and New York came just in time for the Fourth of July. Newspapers were full of hasty rumors. The Indianapolis Star told its readers that the would-be assassin, now identified as Frank Holt from Ithaca, was a “crack-brained teacher, believing himself the agent of God to stop the flow of munitions to Europe” — and that he had also targeted President Wilson, which was not true. Much of the news flashed through the press came from a confession Holt gave to a New York bomb detective. That confession made him seem like a pacifist, bent not on extinguishing but saving human lives.

(Indianapolis Star, July 4, 1915.)

(Indianapolis Star, July 4, 1915.)
By July 6, investigators had begun to believe that Frank Holt was identical with the long-lost “Harvard Wife Murderer,” Erich Muenter, missing for nine years. As Muenter’s incredibly successful mask fell off, he tried to kill himself in jail, slashing his wrists with a lead pencil. The Cornell professor successfully committed suicide on July 6 at a jail in Mineola on Long Island by jumping to a concrete floor, though reports about his suicide varied, some saying that he cracked his skull and “dashed his brains out,” others claiming that he ate a percussion cap, since a loud explosion was heard in his cell.
“Frank Holt” wrote a death note to his wife back in Texas, which read: “Pray that the slaughter will stop,” a reference to the European war. Newspapers reported that the dead man was slated to become head of Southern Methodist University’s French department that fall. A large cache of explosives thought to belong to him had just been found on West 38th Street in New York.

(Evansville Press, July 6, 1915.)
News readers must have been driven mad by the twists and turns of the thrilling tale, especially as the anti-war “agent of God” metamorphosed into a bizarre fugitive and “uxoricide” (wife-murderer), then an Ivy League professor, then… a ship bomber.
In his suicide note, Muenter told his wife that while en route from the U.S. Capitol to Long Island, he stopped in New York and put several half-pound sticks of dynamite on an oceangoing vessel bound for Europe. Holt didn’t say which vessel, but it was loaded with sailors and ammunition. Wireless signals frantically fired the information out to sea, warning captains and crew to search their cargo holds for a bomb. On July 9, 1915, two days after Muenter’s suicide and on the very day he predicted there would an explosion, the SS Minnehaha caught fire after a blast. (The Minnehaha had been built by the same Belfast company that constructed the Titanic and was once sailed on by Mark Twain.) The blast in the ship’s hold caused a dangerous fire but failed to ignite the high explosives on board. The vessel scurried into Halifax harbor. Ironically, two years later, in September 1917, the Minnehaha was torpedoed by a German U-boat off the southwest coast of Ireland, just a few miles from where the Lusitania went down with 1,200 innocent lives.

(The SS Minnehaha carried weapons from the U.S. to Britain. Bombs were also reported on several other steamers.)

(Indianapolis News, July 7, 1915.)
Handwriting experts connected some more dots, giving further evidence that Frank Holt and Erich Muenter were one and the same.
Back in Texas, Leona Holt was in shock. Her family refused to believe that Frank was the “Harvard wife murderer” — ironically, Muenter’s family and Chicago in-laws had had the same reaction after his first wife’s death in 1906. Leona blamed her husband’s severe headaches, overwork, and the effects of skeletal tuberculosis. She was also quick to urge that he “had no Socialist tendencies.” His father-in-law, Dr. O.F. Sensabaugh, insisted that Frank was from Wisconsin and, though he may have been a German sympathizer, he could never have been the Harvard poisoner. Touchingly, Sensabaugh added that even “If Holt really was a man who had dropped to life’s bottom — and I can’t believe it — I take my hat off to him for the way he came back. No man could have been a more lovable husband and father and a better friend than he was while I knew him.” Friends and family were convinced this was all an incredible case of mistaken identity.
The U.S. Army, however, had to station a guard over Muenter’s gravesite at Dallas’ Grove Hill Cemetery to prevent desecration of the body. The name on the tombstone still reads “Frank Holt.”
The press soon printed allegations that the fugitive Muenter, possibly a real psychopath after all, had sent a letter from New Orleans in 1906 threatening to “annihilate” Chicago and Cambridge for accusing him of poisoning his first wife — and that the real reason he fled Massachusetts was to escape the severe punishment that state inflicted on Christian Scientists whenever a death occurred after refusing medical treatment.

(Indianapolis Star, July 8, 1915. Muenter’s daughter Leona, born just days before her mother’s murder in 1906, lived in Chicago and was active in Democratic Party politics there into the days of Mayor Richard Daley. She died as recently as 1996.)
The truth behind the tragic 1906 murder in New England — whose long shadow eventually spread over a Texas family, a powerful Wall Street tycoon, a U.S. vice-president, and others — may never be fully known. But Erich Muenter’s subterfuge led to one of the oddest and most twisted news stories ever covered by the press.
Whether Germany’s sympathizers were right or not, the actions of its saboteurs and spies on American soil — which led to some fascinating rumors about the Kaiser’s cross-dressers in New York — did nothing to help “the Fatherland.” By 1917, when America finally declared war on Germany, such actions and the press’ role in portraying “Hun barbarity” fueled the equally frightening anti-German hysteria that gripped the country.
Chronicling America has put together a list of related news articles on Erich Muenter’s “Reign of Terror.”
Contact: staylor336 [AT] gmail.com
Like this:
Like Loading...





















































































 The Ogden Standard-Examiner, Ogden, Utah, February 11, 1923.
The Ogden Standard-Examiner, Ogden, Utah, February 11, 1923.
















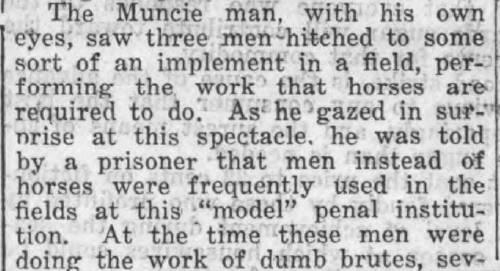 Muncie Post Democrat, August 4, 1922.
Muncie Post Democrat, August 4, 1922.