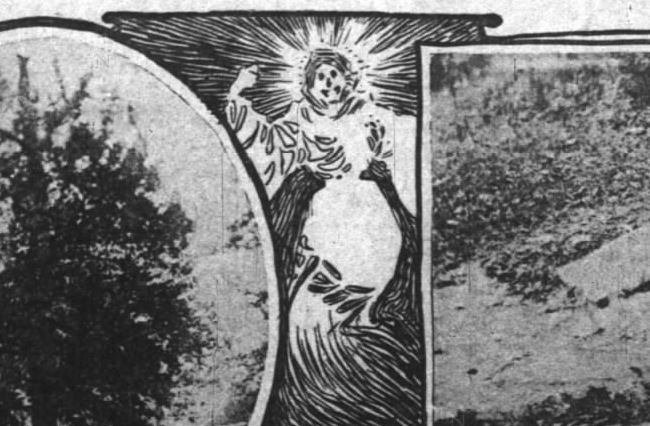
You like alphabet soup? Well, if an anarchist chef prepared it, you’d better take your spoon and dig out these letters first: A-R-S-E-N-I-C.
You like alphabet soup? Well, if an anarchist chef prepared it, you’d better take your spoon and dig out these letters first: A-R-S-E-N-I-C.
One of the weirdest stories ever to spill out of the annals of Midwestern crime is the tale of a bumbling European anarchist named “Jean Crones” who, at a banquet in Chicago in 1916, attempted to assassinate the city’s Roman Catholic archbishop, the Governor of Illinois, and three-hundred priests, bankers, and city officials — not with bullets, but with bouillon. The “soup poison plot” belongs in any encyclopedia of infamy. It’s also a fascinating glimpse into one of American labor’s most turbulent decades. Yet few have ever heard of it. As part of our ongoing series on hoaxes, hysteria and rumors in the news, Hoosier State Chronicles wants to resurrect this old, mostly forgotten story.
When modern anarchism came to the U.S. in the late 1800s, it was closely tied to the struggles of German, Italian, and East European immigrants. While hurling bombs and bullets was an ill-considered way to foster social justice, the conditions these immigrants faced were dire and very real. Anarchism’s philosophical roots, however, were among Europe’s elite. (One early proponent of anarchy was the British philosopher William Godwin, husband of feminist writer Mary Wollstonecraft and the father of Frankenstein‘s author, Mary Shelley.) Iron-fisted reactions to Europe’s 19th-century revolutions spurred philosophers and workers to declare that “Property is Theft” and to strive for the abolition of all governments, including democracies. Because anarchists promoted ideas like “free love” (which critics confused with promiscuity), state and church authorities tried to wipe them out.
While few anarchists ever committed outright acts of murder and mayhem, extremists occasionally wreaked havoc on American cities and police forces. By the time of World War I, headlines about real and mythical anarchist bomb plots were common news.
Since most anarchists had immigrated from countries with state religions, their animosity toward priestly authority should come as no surprise. During the Russian Revolution and on into the 1920s and ’30s, radicals (anarchists among them) in Russia, Mexico and Spain launched all-out wars on religion, desecrating churches and even “executing” statues of Jesus, not to mention priests and nuns, who often suffered especially macabre fates.
Yet if Chicago’s anarchists had wanted to assassinate any powerful “prince of the Church” in 1916, the worst choice was probably George Mundelein.

Mundelein was born in a poor working-class immigrant neighborhood, Manhattan’s Lower East Side, in 1872 and grew up in tenement housing. Son of a German father and Irish mother, his dual ethnic heritage was a major reason why, in 1915, the young Bishop of Brooklyn was chosen to head the Chicago archdiocese, ethnically diverse and also teeming with ethnic conflict even among fellow Catholics. At age 43, Mundelein was the youngest American archbishop. Over the years, the leader of Chicago’s Catholics turned out to be a major pro-labor voice, an important ally of Franklin Roosevelt’s New Deal, and a staunch enemy of Nazism and anti-Semitism — including that of Father Charles Coughlin, a controversial American radio priest whose show, broadcast out of Detroit, often attacked Jews and bankers. A friend of the Catholic Labor Movement, Mundelein reiterated to American Catholics that “our place is beside the workingman.”
George Mundelein, then, was a rather strange target for an aspiring assassin’s vial of poison on February 12, 1916. The scene of the crime: Chicago’s prestigious University Club.


Coming together to honor both Abraham Lincoln’s birthday and Mundelein’s installment as Chicago archbishop, about three-hundred guests attended — from Illinois Governor Edward F. Dunne and ex-Governor Charles Deneen to Chicago’s ex-Mayor Carter Harrison, Jr. Most of the other guests were Catholic priests from all over the U.S.
As Chicago’s health commissioner, city police investigators, and a chemist from the University of Chicago later determined, someone that day slipped enough arsenic into a pot of chicken bouillon to kill two-hundred people or more. Various accounts floated around of how the University Club avoided becoming the scene of what would still be the biggest mass murder in Chicago history — worse even than the crimes of the “arch-fiend” H.H. Holmes back in the 1890s.
One version of the tale was that a “miracle” occurred. At the last minute, ninety-six guests showed up unexpectedly, prompting kitchen staff to resort to a time-honored remedy: watering down the soup. Yet apparently the real disaster was averted by slow, talkative eaters. As Monsignor Evers, pastor of St. Andrew’s Church in New York, told the Chicago Daily Tribune, some guests were “so engrossed in conversation” that they missed out on the soup altogether or had only eaten a spoonful or two by time their neighbors started to have stomach cramps.

With many diners complaining of sudden stomach pains, a doctor at the banquet suspected that the animal fat used to prepare the soup stock must have gone sour — normal food-poisoning, in other words. He went to the kitchen and quickly prepared an “emetic of mustard” to induce vomiting. The result is unappetizing to consider, but the elegant dining room must have become a surreal and disgusting scene. Yet the doctor’s speedy remedy probably saved many lives. Scores of guests were sickened, some violently, but only one guest, Father John O’Hara of Brooklyn, died. Archbishop Mundelein himself was unaffected by the lethal soup, but Chicago authorities kept him under a guard of 150 mounted police and detectives for the next few days.

Police quickly traced the foiled murder plot to a certain “Jean Crones,” assistant chef at the University Club, said to be about 30 years old. Crones “often inveighed” against social inequality, said the Club’s officials. When police raided his apartment, Crones the “souper anarchist” was gone, but investigators discovered a stash of anarchist literature (“a library of hatred,” says one paper), a chemical laboratory and all the evidence of poison they needed to go after him.
As the manhunt for Crones spread out, he or someone masquerading as him began to tease the police with flippant, irreverent letters, taunting the cops for being unable to find him. These letters and other baffling clues began to pour in from all parts of the country. When the story made national news the next day, a hotel in Binghamton, New York, reluctantly announced that it was confident Crones had been their assistant chef. “Crones was remembered by his fellow workers here as a dabbler in chemistry and photography. . . One day the whim seized him to have his own likeness snapped, and he had one of his kitchen comrades aim the camera.” That photo and an artist’s sketch were plastered over many American newspapers.
What happened next rapidly turned into a comedy of errors — one that went on for years.

During the run-up to World War I, when the loyalty of German-Americans constantly fell under suspicion, unfounded reports came in that Crones was a German immigrant, a saboteur and spy for the Kaiser. Other reports insisted that he was French or Italian. A biography of celebrated anarchists Sacco and Vanzetti claims that “Jean Crones” was an Italian named Nestor Dondoglio. Chicago’s Police Department officially called off its search for the mysterious fugitive in 1919. Yet Dondoglio evaded police until 1932, when he died on a farm in Connecticut where an Italian family had given him shelter.
Whatever the elusive truth behind Crones identity was, for several years after the failed “soup plot” he became a sort of comedic bogeyman, stalking America from sea to shining sea. Souper spottings occurred all over: in rural Mt. Airy and Oxford, North Carolina; in the mining town of Leadville, Colorado; and in towns so obscure they weren’t even spelled right in newspapers (like Spalding, Nebraska, and Moberly, Missouri.) Crones — or a clever prankster, or a whole team of anarchists — harassed the police from New York City to Portland, Oregon. A chef from Iowa City was arrested simply because he looked like the photograph snapped at a kitchen in Binghamton, as was another chef from Chicago while passing through Springfield, Ohio.
Illinois State Attorney Maclay Hoyne surmised that the “poison souper” invented something called the “McKinney-Finn powders… given by waiters to non-tipping patrons in local hotels and cafes.”
Most of the so-called “appearances” of Jean Crones, however, are probably imaginary — or even deliberate hoaxes. In some cases, it even sounds like the police might have used the poison-souper scare as an excuse to terrorize workers. Others had more comic twists.




Within a few days of his apparent escape from Chicago, the phantom assassin or his clever doppelgänger was on the West Coast, teasing Chicago police from a distance, mailing them his own fingerprints and threatening to kill “some bishop” out in Oregon:

On St. Patrick’s Day that March, Chicago Catholics were still so jittery that the Irish Fellowship Club had to appoint an official food taster for its annual banquet. He tasted every dish for over an hour. And survived.
It’s very possible that prank-minded Americans were just having fun with the police and the press. Yet by the summer of 1916, the spate of “J.C.” sightings was still pouring in:


Two of the most humorous and unlikely sightings occurred on the East Coast. In Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, that May, locals were convinced that Crones had become a nun:


And in Luzon, New York, an undercover sleuth wearing false hair and whiskers was arrested by a town cop who was confident he had nabbed the elusive Crones at last. The man turned out to be a 26-year-old private eye from New York City, busy investigating a theft of $250 from the Hygienic Brush Company. In spite of this legitimate alibi, county prosecutors charged the man with “masquerading.”

The real Jean Crones never surfaced. Yet the fictional specter he evoked — that of the violent, supposedly illiterate immigrant bent on destroying American institutions and lives — took on a frightening reality of its own at a time when immigrant loyalty was suspect.
It’s often forgotten that the Communist witch hunts inaugurated by Senator Joseph McCarthy in the 1950s were preceded by a more substantial “Red Scare” after World War I. In 1929, Italian anarchists detonated bombs in Washington, D.C. — an attack that nearly killed Franklin and Eleanor Roosevelt — and possibly carried out the 1920 Wall Street attack, which killed 30 people. The reaction threatened to close America’s doors to immigrants.
Like most Catholics, Archbishop Mundelein was a strong supporter of immigration. He blew off threats of assassination by anarchists and the hostility of anti-Catholics, saying: “I have come to Chicago to help and bless its people all I can, and I think this is the best way to disarm prejudice.”
A fiery and brilliant editorial in the Kentucky Irish American, a pro-immigrant paper published in Louisville, conjures up the fear that the figure of “Jean Crones” actually created among nativists. For immigration’s enemies, the anarchist threat was reason enough for Congress to all but close down Ellis Island. (Ironically, the Hans Schmidt mentioned in this passionate editorial was a German-American Catholic priest convicted of murder, then sent to the electric chair at Sing Sing on February 18, 1916. Schmidt’s execution occurred just a week after the anarchist soup plot in Chicago.)

Kentucky Irish American, April 15, 1916.
Cardinal Mundelein, the target of one of those rare immigrants who turned to violence, spent the next few decades speaking out on behalf of the working poor. Perhaps the shocking event at the start of his days as leader of Chicago’s Catholics brought home the need for justice in his city and elsewhere.
He died in his sleep in October 1939, an honored man.